••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Data Mining Techniques for Detecting Household Characteristics Based on Smart Meter Data
Abstract
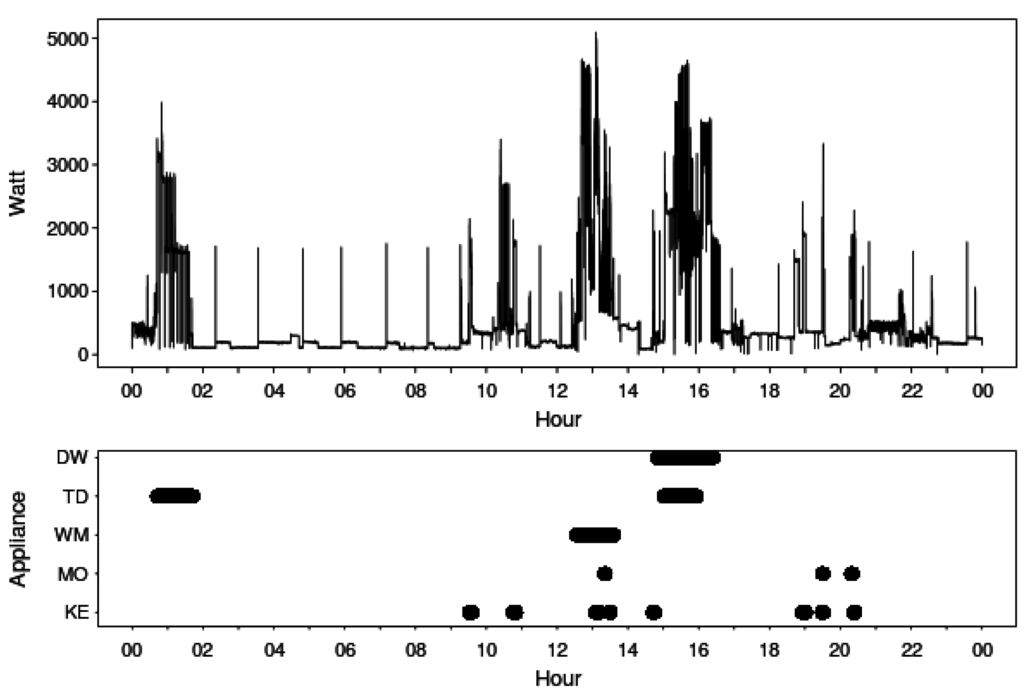
The main goal of this research is to discover the structure of home appliances usage patterns, hence providing more intelligence in smart metering systems by taking into account the usage of selected home appliances and the time of their usage. In particular, we present and apply a set of unsupervised machine learning techniques to reveal specific usage patterns observed at an individual household. The work delivers the solutions applicable in smart metering systems that might: (1) contribute to higher energy awareness; (2) support accurate usage forecasting; and (3) provide the input for demand response systems in homes with timely energy saving recommendations for users. The results provided in this paper show that determining household characteristics from smart meter data is feasible and allows for quickly grasping general trends in data.
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Streamlining Smart Meter Data Analytics
Streamlining Smart Meter Data Analytics
Xiufeng Liu and Per Sieverts Nielsen Technical University of Denmark
{xiuli, pernn}@dtu.dk
Abstract. Todaysmartmetersareincreasinglyusedinworldwide.Smartmetersaretheadvancedmetersca- pable of measuring customer energy consumption at a fine-grained time interval, e.g., every 15 minutes. The data are very sizable, and might be from different sources, along with the other social-economic metrics such as the geographic information of meters, the information about users and their property, geographic location and others, which make the data management very complex. On the other hand, data-mining and the emerging cloud computing technologies make the collection, management, and analysis of the so-called big data possible. This can improve energy management, e.g., help utilities improve the management of energy and services, and help customers save money. As this regard, the paper focuses on building an innovative software solution to stream- line smart meter data analytic, aiming at dealing with the complexity of data processing and data analytics. The system offers an information integration pipeline to ingest smart meter data; scalable data processing and analytic platform for pre-processing and mining big smart meter data sets; and a web-based portal for visualiz- ing data analytics results. The system incorporates hybrid technologies, including big data technologies Spark and Hive, the high performance RDBMS PostgreSQL with the in-database machine learning toolkit, MADlib, which are able to satisfy a variety of requirements in smart meter data analytics.
Keywords: Streamline, Software Platform, Smart meter data, Data Analytics
http://orbit.dtu.dk/files/110737589/Streamlining_Smart_Meter_Data_Analytics.pdf
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Clustering Time‐Series Energy Data from Smart Meters
Alexander Lavin1, Diego Klabjan2
Abstract
Investigations have been performed into using clustering methods in data mining time‐series data from smart meters. The problem is to identify patterns and trends in energy usage profiles of commercial and industrial customers over 24‐ hour periods, and group similar profiles. We tested our method on energy usage data provided by several U.S. power utilities. The results show accurate grouping of accounts similar in their energy usage patterns, and potential for the method to be utilized in energy efficiency programs.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.07602.pdf
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Utilities ‘Very Excited’ about Mining Smart Meter Data and Invading Your Privacy
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.07602.pdf
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Applying Smart Meter and Data Mining Techniques to Predict Refrigeration System Performance
Jui-Sheng Chou , Anh-Duc Pham
A major challenge in many countries is providing sufficient energy for human beings and for supporting economic activities while minimizing social and environmental harm. This study predicted coefficient of performance (COP) for refrigeration equipment under varying amounts of refrigerant (R404A) with the aids of data mining (DM) techniques. The performance of artificial neural networks (ANNs), support vector machines (SVMs), classification and regression tree (CART), multiple regression (MR), generalized linear regression (GLR), and chi-squared automatic interaction detector (CHAID) were applied within DM process. After obtaining the COP value, abnormal equipment conditions can be evaluated for refrigerant leakage. Analytical results from cross-fold validation method are compared to determine the best models. The study shows that DM techniques can be used for accurately and efficiently predicting COP. In the liquid leakage phase, ANNs provide the best performance. In the vapor leakage phase, the best model is the GLR model. Experimental results confirm that systematic analyses of model construction processes are effective for evaluating and optimizing refrigeration equipment performance.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417413007446
Cluster Analysis of Smart Metering Data An Implementation in Practice
Authors : Dipl.-Wi.-Ing. Christoph Flath Dipl.-Wi.-Ing. David Nicolay, Dr. Tobias Conte, PD Dr. Clemens van Dinther, Dr. Lilia Filipova-Neumann
Research Center for Information Technology
Haid-und-Neu-Str. 10–14, 76131 Karlsruhe Germany
Utilities and electricity retailers can benefit from the introduction of smart meter technology through process and service innovation. In order to offer customer specific services, smart meter mass data has to be analyzed. In the article we show how to integrate cluster analysis in a business Intelligence environment and apply cluster analysis to real smart meter data to identify detailed customer clusters.
A Data Mining Framework for Electricity Consumption Analysis From Meter Data
Article in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Information – September 2011
Abstract
This paper presents a novel data mining framework for the exploration and extraction of actionable knowledge from data generated by electricity meters. Although a rich source of information for energy consumption analysis, electricity meters produce a voluminous, fast-paced, transient stream of data that conventional approaches are unable to address entirely. In order to overcome these issues, it is important for a data mining framework to incorporate functionality for interim summarization and incremental analysis using intelligent techniques. The proposed Incremental Summarization and Pattern Characterization (ISPC) framework demonstrates this capability. Stream data is structured in a data warehouse based on key dimensions enabling rapid interim summarization. Independently, the IPCL algorithm incrementally characterizes patterns in stream data and correlates these across time. Eventually, characterized patterns are consolidated with interim summarization to facilitate an overall analysis and prediction of energy consumption trends. Results of experiments conducted using the actual data from electricity meters confirm applicability of the ISPC framework.
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
In-Home Surveillance Using Smart Meters. Privacy, Data Mining and Health Impacts
A look at what utility companies, PUCs, and the former CIA director have to say about the ‘smart’ meters, data-mining, and surveillance — sans propaganda.
It’s always a drag to find out when a friend is saying one thing to your face, and another to your back. As uncovered in our film Take Back Your Power, the way in which most utilities are now delivering the lies and propaganda — with your individual rights, security, and potentially health on the line — is elevating the trait of “two-faced” to a completely new level.
It’s important to note that the first 4 of these references have to do with the smart meters / grid infrastructure capabilities as of this time. According to the sum of my research over the past 3 years, the plan involves achieving a greater and greater level of granularity and extraction of in-home data over time — see #5 and #6 below as examples (as well as my article on Google’s Nest acquisition). So as far as privacy and surveillance go, according to utilities’ own documentation and writings, ‘smart’ meters are effectively a trojan horse.
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
“Data is ALWAYS worth money. Companies pay BIG money for information on your buying habits, for your email address, and more. Technically, according to one of the Smart Meter experts I talked with, Smart Meters could track what TV shows you watch, and potentially what food you eat, if your refrigerator is equipped with “Smart” technology.” – Smart Meters Exposed
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Researchers find smart meters could reveal favorite TV shows
Tests on smart meters made by German company Discovergy show that someone with network sniffing skills and equipment could determine what’s been watched by looking at lighting display patterns.
“”Our test results show that two 5-minute chunks of consecutive viewing without major interference by other appliances is sufficient to identify the content,” Loehr and his fellow researchers–Ulrich Greveler and Benjamin Justus–wrote in their paper, to be presented Wednesday at the Computers, Privacy and Data Protection conference in Brussels.”
“The data is exposed because it is not signed or encrypted, Loehr said in an interview with CNET. “Anyone with access to your home network has access to this data,” he said.”
https://www.its.fh-muenster.de/greveler/pubs/preprint_online.pdf
source : http://www.cnet.com/news/researchers-find-smart-meters-could-reveal-favorite-tv-shows/
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Onzo looks for the details in the Data
from 4:03-5:24, explains the concerns about data mining from Onzo

